How to boot from a bootable Recovery USB and recover the boot loader.
This is useful if you cannot boot your Operating System from disk.
Please note: You can follow this guide to create a bootable USB drive.
1 Cannot boot
If you can't access your operating system or its recovery menu, it can be repaired from a bootable USB drive.
Firstly, insert the USB drive and turn on your computer whilst repeatedly tapping the F7 key.
This will bring up the boot menu.

2 Boot Recovery USB
Use the arrow keys to select your USB drive and press enterto boot from it. You need to use the live mode of the USB. There are a few different terminologies used but typically it is Live, Tryor **Start.**On Ubuntu, the option to select is Try Ubuntu.

3 Check disk path
Open the GNOME Launcher and open Terminal.

To check the path of the disk, type in the below command:
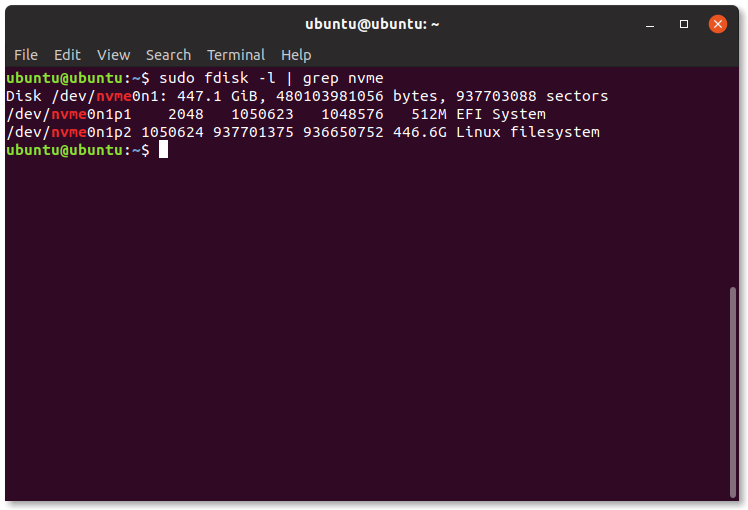
sudo fdisk -l | grep 'nvme|sda'
4 Partition of disk
This will reveal the partition of the disk that needs mounting. This will either reveal sda or nvme
5 Mount partitions
Most installs will only have the 2 partitions shown.
Run the below commands to mount them:
sudo mount /dev/nvme0n1p2 /mnt
sudo mount /dev/nvme0n1p1 /mnt/boot/efi
sudo mount --bind /dev /mnt/dev
sudo mount --bind /dev/pts /mnt/dev/pts
sudo mount --bind /proc /mnt/proc
sudo mount --bind /sys /mnt/sys
6 Enable network
Depending on what you need to do in the recovery mode, you may want to enable internet access with:
sudo cp /etc/resolv.conf /mnt/etc/resolv.conf
7 Connecting to installation
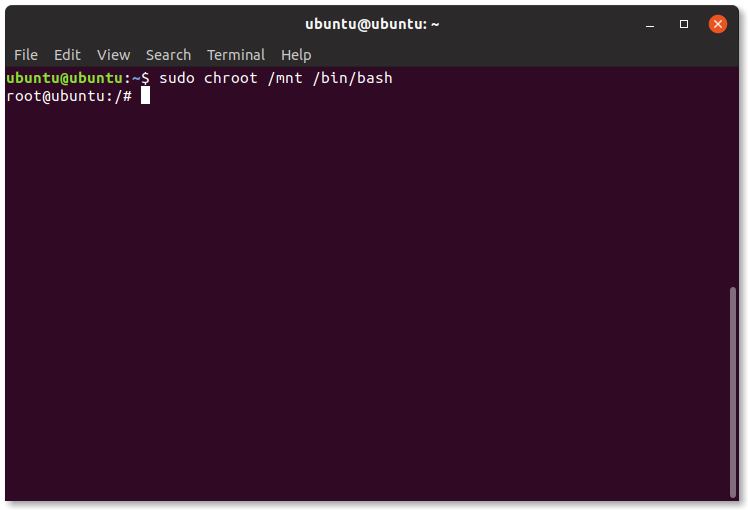
From here, we need to chroot into the disk with:
sudo chroot /mnt /bin/bash
8 Connected to installation
This will take you to a terminal window running as root on your SSD.
9 Ready to diagnose
From here we are ready to perform further diagnostics on the installation.
- fsck - Check file system
- GRUB Repair - Update bootloader
- dpkg - Repair broken packages
The most common reason for attempting recovery from a USB drive is an interrupted update - which results in getting stuck at a grub prompt. To resolve this issue, enter the below commands:
sudo dpkg --configure -a
sudo apt -f install
See further guide on using recovery mode
